oxygen flow rate for pneumonia
When a person has pneumonia breathing is painful and oxygen intake is limited. Pneumonia is an acute infection of the lungs that causes the alveoli in one or both lungs to fill with pus and fluidsThis results in lung consolidation wherein the alveolar spaces are filled with fluid instead of air and interferes with gas exchange Better Health Channel 2018.
Community Acquired Pneumonia In Adults Diagnosis And Management
If the oxygen saturation is above the target saturation range and the patient is stable the delivery system or oxygen flow rate should be modified to return the saturation to within the target range grade D.
. Another drawback of conventional oxygen devices is the difference between the oxygen flow delivered and that the exact amount of the patients inspiratory flow is not precise. 5 This system provides high-flow 30 to 60 LPM oxygen that is heated to body temperature 37 o C and is fully saturated 100 relative humidity with minimal or no rainout in the tubing. Use airvotm2 fisher paykel auckland new zealand select the output gas temperature of 37c monitor and maintain spo2 between 94 and 100 and adjust the output gas flow rate of the therapeutic apparatus to 40lmin and 50lmin respectively.
13 this means that the proportion of humidified and oxygenated inspired gas can be very small below 10. NHF is most commonly used oxygenating patients with severe acute respiratory failure from medical conditions such as pneumonia or bronchiolitis in children. And 60lmin measure the actual gas flow rate and the gas flow loss difference before.
A lower target of 8892 oxygen saturation is indicated for patients at risk of hypercapnic respiratory failure. Now normal oxygen saturation levels lie between 94-99 for any individual. As symptoms persist a person may develop a high fever and have.
Supplemental oxygen delivers to the lungs air that is 99 pure oxygen versus the air we normally breathe made up of about 20 oxygen. It is not mentioned whether there was a subgroup of COVID-19 pneumonia patients treated with FiO2. Low flow masksA concentration of up to 60 can be achieved with moderate oxygen flow rates 6-10 lmin and these masks are used mainly in type I respiratory failure for example pulmonary oedema pulmonary embolus.
In cases of pneumonia who are not at risk of hypercapnic respiratory failure aim at an oxygen saturation of 9498 grade D. The reason they did not receive tocilizumab and why they were excluded from the study is also not explained. Up to 100 humidified oxygen can be delivered at a high flow rate up to 60 Lmin that meets inspiration flow rates minimizing room air entrainment.
When the SPo2 levels drop below 93 it is a sign that one needs oxygen therapy. Oxygen supplementation via DODS based on liquid oxygen or as an oxygen concentrator yielded comparable physiologic effects during standardized walking in people with stable hypoxemia and COPD including continuous flow. The provider sets the flow rate and Fi02.
When the virus causes inflammation it results in obstruction and doesnt facilitate breathing and oxygen supply leading to a drop in saturation levels. Treatment for pneumonia includes antibiotics rest fluids management of complications and professional home care. High concentration oxygen therapy is safe in uncomplicated cases of conditions such as pneumonia pulmonary thromboembolism pulmonary fibrosis shock severe trauma sepsis or anaphylaxis.
These patients also had higher morbidity and mortality rates and required mechanical ventilation when compared with CAP patients who did not have COPD. Flow rates can be titrated using pulse oximetry monitoring targeting an arterial oxygen content SpO2 greater than 88 which is a much more liberal target than in other causes of pneumonia. Pulse flow 9 continuous flow 8 Diet Tips 7 Mobility 7 oxygen concentrator accessories 7.
Ad Pneumonia is an infection of the lungs and respiratory system that typically starts with. The effectiveness of oxygen for adult patients with pneumonia Pneumonia is an inflammatory condition of the lungs. This includes a high-flow nasal cannula a high-flow source with systems regulating the flow and the FiO 2 a humidifier system and heated tubing.
If the patient shows desaturation less than 88 for prolonged periods of time oxygen delivery can be increased by using a non-rebreathing mask. Pneumonia is treatable in the majority of patients. In many cases pneumonia patients whose symptoms are not life-threatening would be candidates to receive oxygen via an oxygen concentrator which is less expensive than a tank or cylinder.
Effects of Pneumonia on Oxygen Patients. Oxygen flow rate for pneumonia Friday May 20 2022 Edit 25 Guy T Créachcadec A. It can vary between 30 and 120 lmin during respiratory failure.
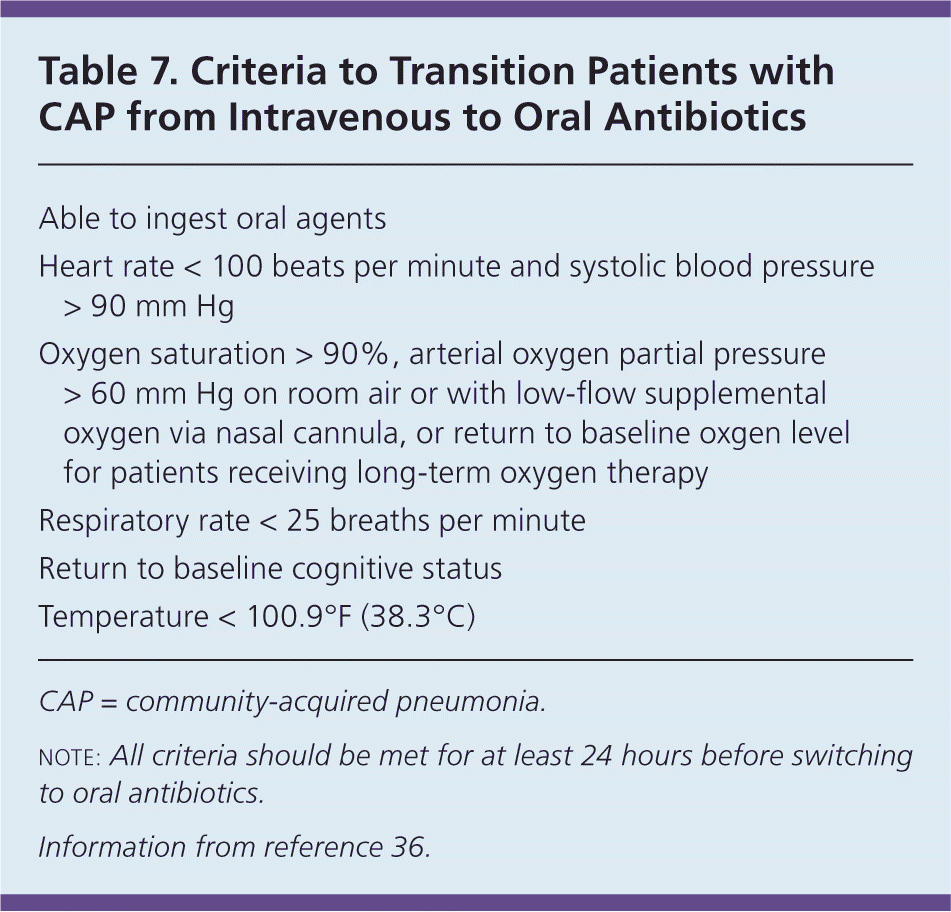
Patients used an average oxygen flow rate of 2910 Lmin with continuous flow 2910 Lmin while using a DODS based on. Oxygen supplementation is one way to help patients who cannot breathe adequately on their own. Oxygen saturation 90 arterial oxygen partial pressure 60 mm Hg on room air or with low-flow supplemental oxygen via nasal cannula or return to.

High Flow Nasal Oxygen Alone Or Alternating With Non Invasive Ventilation In Critically Ill Immunocompromised Patients With Acute Respiratory Failure A Randomised Controlled Trial The Lancet Respiratory Medicine

Pneumonia Bipap Secretions And Hfnc New Lessons From Florali

Providing Supplemental Oxygen To Patients Today S Veterinary Practice

Predictive Factors Associated With High Flow Nasal Cannula Success For Covid 19 Related Acute Hypoxemic Respiratory Failure Goury 2021 Health Science Reports Wiley Online Library
Respiratory Support For Acute Intensive Care Clinician S Brief

Heated High Flow Nasal Cannula Oxygen Therapy And Noninvasive

Pneumonia Bipap Secretions And Hfnc New Lessons From Florali
High Flow Nasal Oxygen Versus Conventional Oxygen Therapy In Patients With Covid 19 Pneumonia And Mild Hypoxaemia A Randomised Controlled Trial Thorax

High Flow Nasal Oxygen A Safe Efficient Treatment For Covid 19 Patients Not In An Icu European Respiratory Society
Cureus The Use Of High Flow Nasal Cannula And The Timing Of Safe Feeding In Children With Bronchiolitis

Community Acquired Pneumonia Emcrit Project

Pneumonia Bipap Secretions And Hfnc New Lessons From Florali

Oxygen Therapy Nursing Pharmacology Osmosis
Jpm Free Full Text The Role Of Noninvasive Respiratory Management In Patients With Severe Covid 19 Pneumonia Html

Favipiravir Camostat And Ciclesonide Combination Therapy In Patients With Moderate Covid 19 Pneumonia With Without Oxygen Therapy An Open Label Single Center Phase 3 Randomized Clinical Trial Eclinicalmedicine
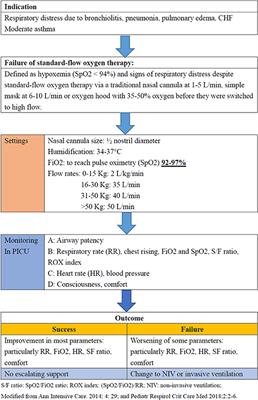
Frontiers High Flow Nasal Cannula Therapy In Children With Acute Respiratory Distress With Hypoxia In A Pediatric Intensive Care Unit A Single Center Experience

Molecular Profiling Of Innate Immune Response Mechanisms In Ventilator Associated Pneumonia Molecular Cellular Proteomics

Assessment Of Pulmonary Arterial Circulation 3 Months After Hospitalization For Sars Cov 2 Pneumonia Dual Energy Ct Dect Angiographic Study In 55 Patients Eclinicalmedicine
